contents area
Public Health Weekly Report
detail content area
- Date2019-10-24 21:38
- Update2019-11-19 17:57
- DivisionDivision of Chronic Disease Prevention
- Tel043-719-7053
Time required from a symptom detection to an arrival at a regional cardiovascular disease centers of stoke or myocardial infarction
◈ This study’s analysis of the time required from First Abnormal symptom detection Time (FAT) to the arrival time at a regional cardiovascular disease center of stroke or myocardial infarction patients who were hospitalized at 11 centers between July of 2016 and December of 2017 showed significant results. The average time required from onsets to arrivals of myocardial infarction patients was far shorter than that of stroke patients (1.3 hours vs. 6.3 hours). In addition, there were significant gaps of the required time of stroke patients between centers (3.7 hours-10.6 hours) (Figure 1).

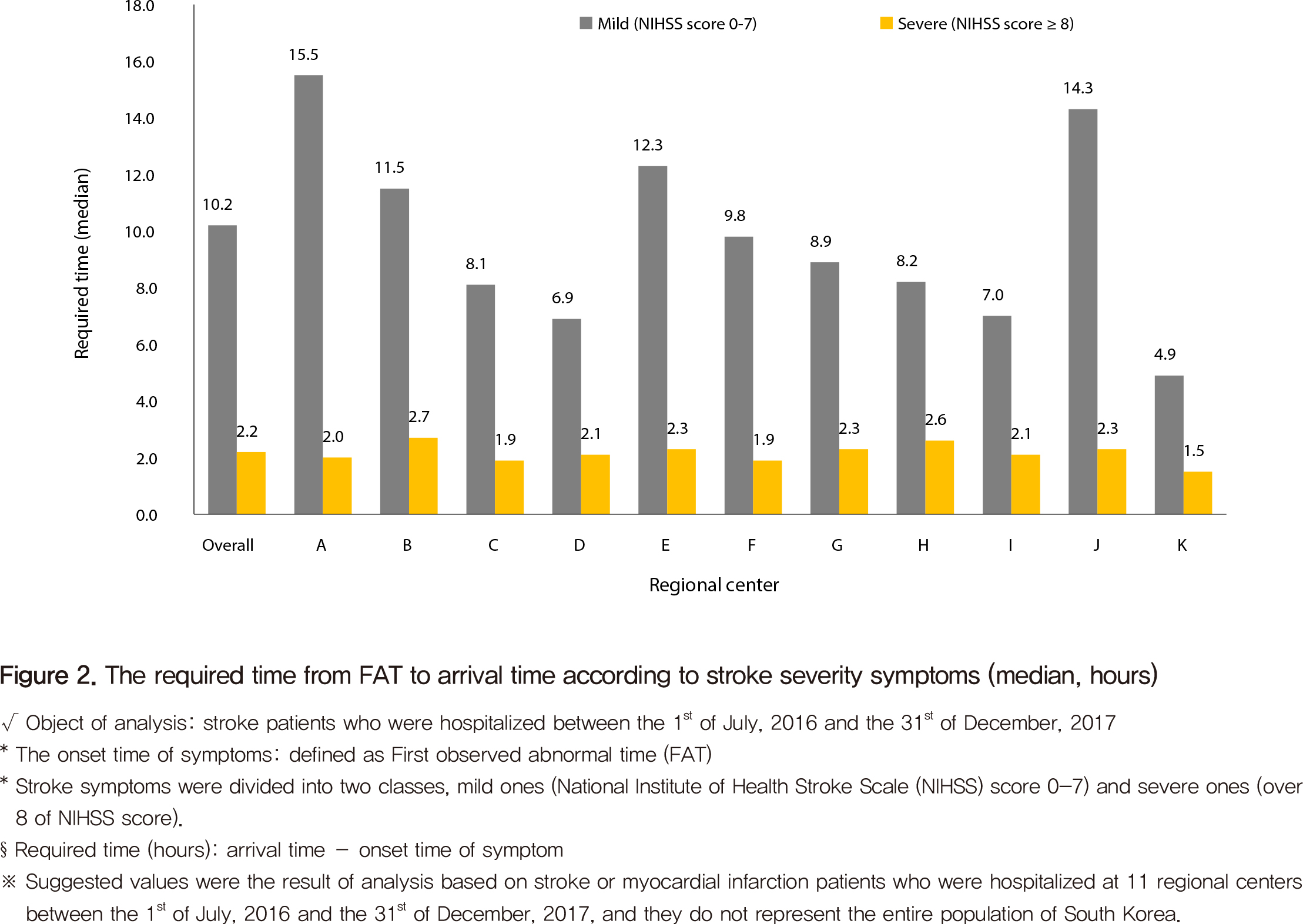
◈ Patients with severe symptoms, such as a loss of consciousness, took a relatively short time, 2.2 hours on average, to arrive at hospitals regardless of region. On the other hand, patients with mild symptoms took a long time on average to arrive at a center and excessive gaps of time between centers were observed (4.9-15.5 hours) (Figure 2).
Source: Ministry of Health and Welfare, Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center 2018 Statistic Repor
* Emergency Department-based Injury In-depth Surveillance: the statistics were calculated based on collected pre- and post-admission data of stroke or myocardial infarction patients hospitalized at 11 regional cardiovascular disease centers each year
Reported by: Division of Chronic Disease Prevention, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 This public work may be used under the terms of the public interest source + commercial use prohibition + nonrepudiation conditions
This public work may be used under the terms of the public interest source + commercial use prohibition + nonrepudiation conditions