contents area
Public Health Weekly Report
detail content area
- Date2019-11-14 23:24
- Update
- DivisionDivision of Chronic Disease Prevention
Prolonged Sitting Time and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes : Rapid literature review
Song Geumju, Kim Il-yeol
Division of Chronic Disease Prevention, Center for Disease Prevention, KCDC
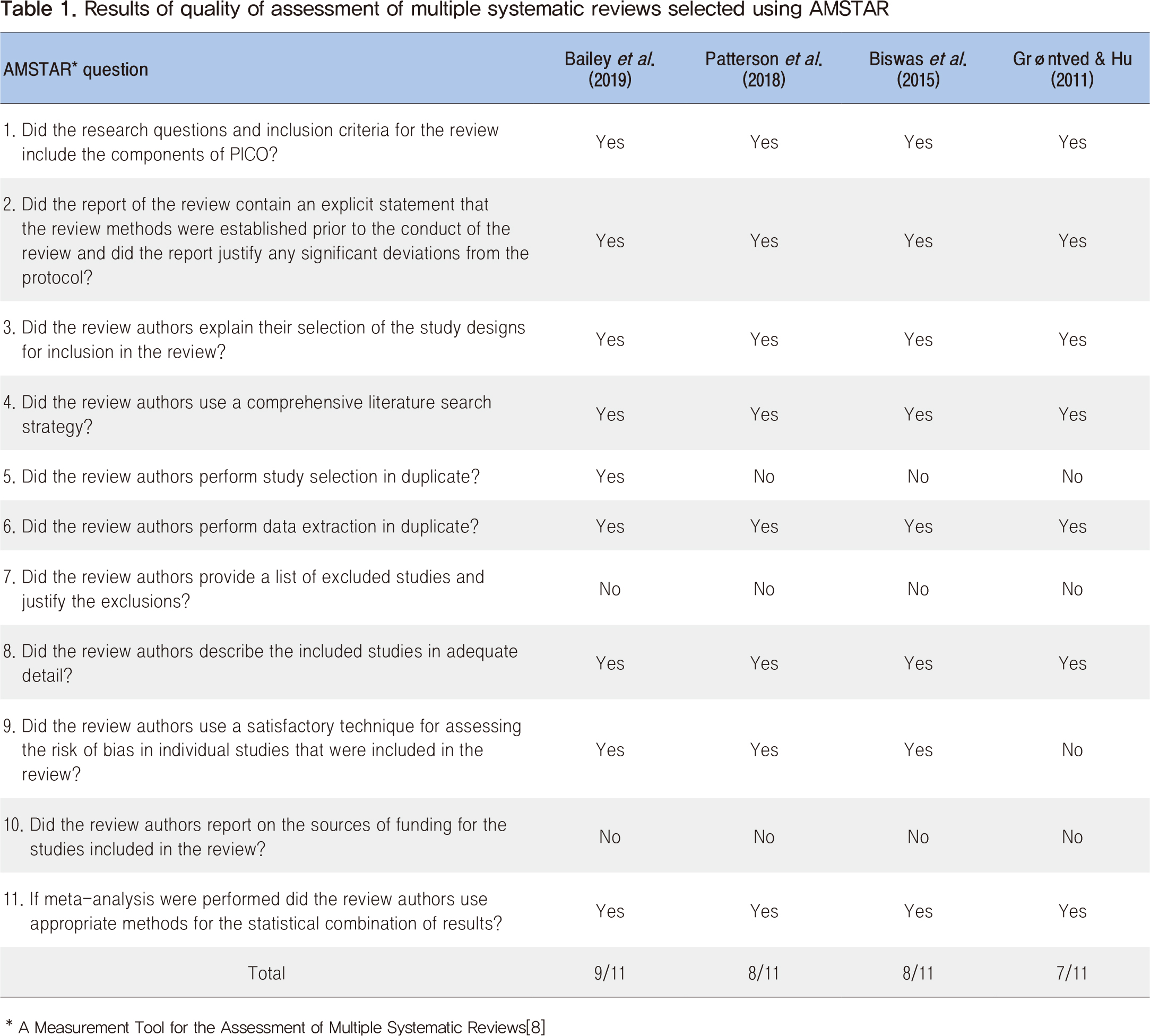
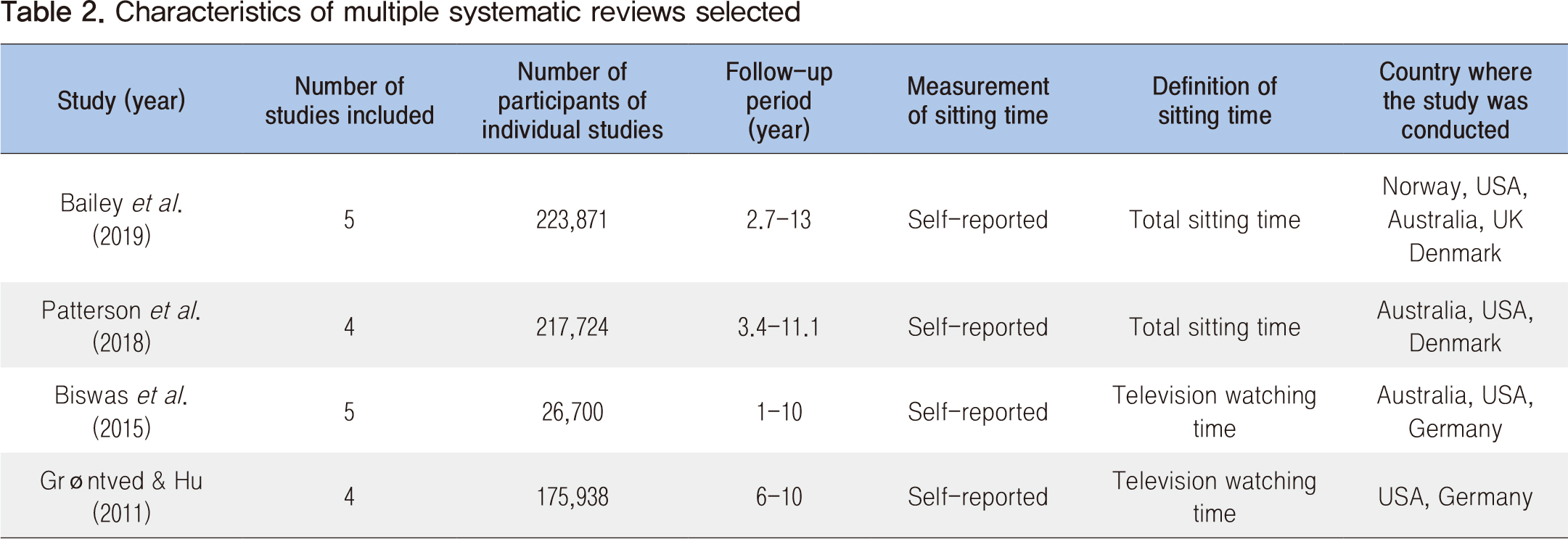
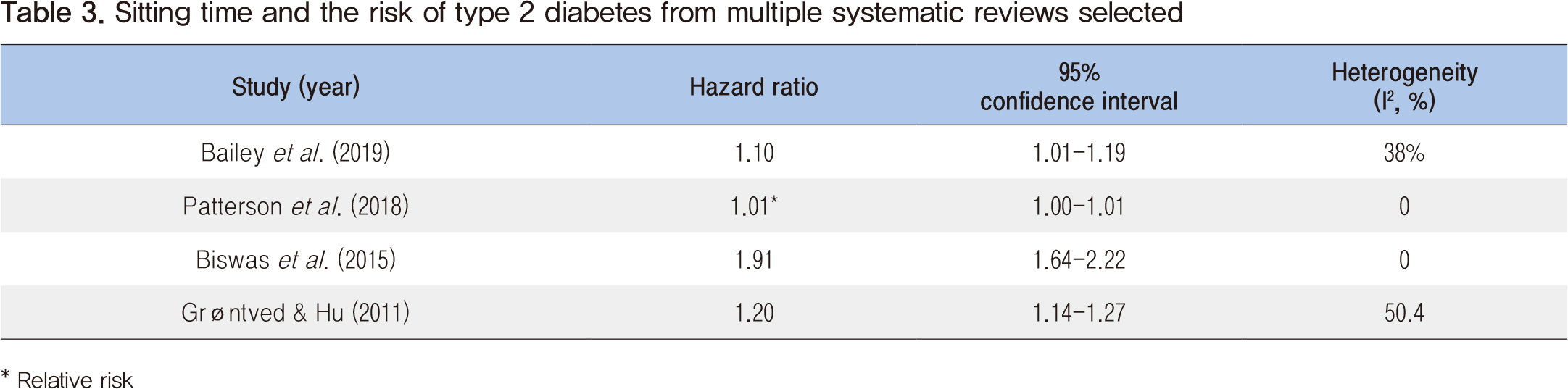
Moderate to vigorous physical activity has conventionally been emphasized to prevent and manage type 2 diabetes; however, recent studies showed that sedentary behaviors such as prolonged sitting time is a behavioral risk factor for type 2 diabetes regardless of the level of physical activity. In order to examine the association between prolonged sitting time and the incidence of type 2 diabetes, four published systematic review studies were reviewed using a rapid literature review method. Study results showed that prolonged sitting time significantly increased the risk of type 2 diabetes. Physical activity guidelines including a specific sitting time with scientific evidence will be needed. Furthermore, the development and promotion of a national level program to reduce sitting time will be needed to prevent and manage type 2 diabetes effectively.
Keywords: Type 2 diabetes mellitus, Sedentary behavior, Systematic review