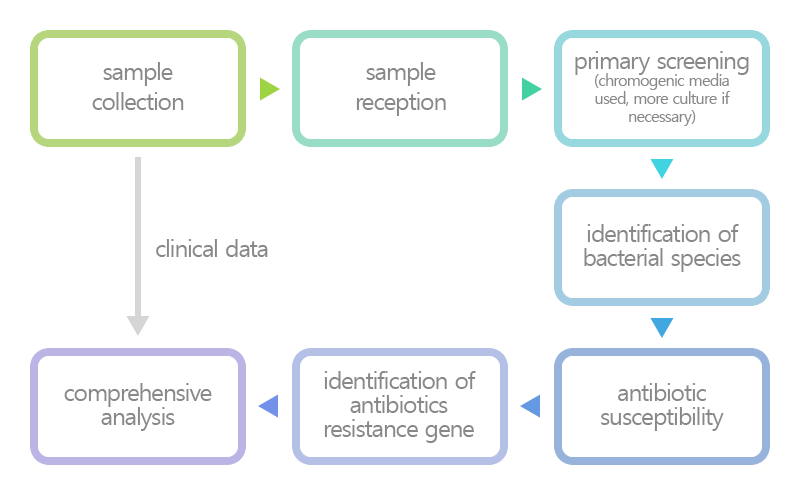
Testing Methods
| Institution in Charge of Preservation | Type of Preservation |
|---|---|
| Research institutions (including the institutions conducting detailed assignments) | 1 skim milk |
| Managing department at KCDC (Department of Antimicrobial Resistance) | 1 skim milk 1 Microbank |