contents area
National TB Elimination Project
detail content area
National TB Elimination
Project
Background
More than 30,000 TB patients are newly reported each year and 2,200 patients die from TB in Korea. The country has the highest TB incidence and mortality rates among OECD member countries. TB, which causes a high disease burden on our society, requires a national control plan. Therefore, the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has been intensively working on the National TB Elimination Project in order to reduce TB incidence rates to levels of advanced countries and protect people from TB.
Introduction
With the vision of “TB Free Society, Healthy Country” based on the Tuberculosis Prevention Act (enacted in 1967 and took effect in 1968), the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention established the TB monitoring system in 2000 and has been conducting the PPM (Public-Private Mix) TB control project since 2007 in order to reduce incidence rates to levels of advanced countries through systematic TB prevention and control. In addition, we have strengthened the duty to report TB patients since 2010 and have established the TB epidemiologic investigation team in 2013 to conduct epidemiologic investigations in institutions such as schools and workplaces. By establishing the “National TB Control Plan (2013),” we have been making efforts for a “TB Free Society, Healthy Country.”
Fluctuation in the number of TB patients
After reaching the highest record in 2011, continuously decreasing from 2012
| Year | 2001 | 2005 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of new cases | 34,123 | 35,269 | 36,305 | 39,557 | 39,545 | 36,089 | 34,869 | 32,181 | 30,892 |
| New TB rate (per 100,000 population) | 71.3 | 72.4 | 72.8 | 78.9 | 78.5 | 71.4 | 68.7 | 63.2 | 60.4 |
| Annual change (%) | - | - | 0.8 | 8.4 | -0.5 | -9.0 | -3.8 | -8.1 | -4.3 |
In spite of our tremendous efforts, we still have difficulty eliminating TB. In 2017, we have carried out the TB Prevention Plan, set up in 2016, in order to prevent and treat latent TB in advance.
Overview
- The details of the “1st National TB Control Plan (2013-2017)” based on the Tuberculosis Prevention Act, PPM TB control project, TB contact surveillance through TB patient monitoring and epidemiologic investigation, and the “TB Prevention Project” started in 2017 are as below.
PPM TB control project
- Selected 120 medical institutions and provided financial support
- Deployed 199 nurses to manage tuberculosis patients
- Intensive control of TB patients with poor compliance treatment and multi-drug-resistant TB patients
Management of close contacts through early detection and epidemiologic investigation
- Conducted epidemiologic investigations when TB patients are detected in schools, medical institutions, social welfare facilities, etc.
- Detected additional TB patients through TB contact investigation and provided checkups and treatment to latent TB infection
Types of Donation and Potential Organs and Tissues
The 1st National. TB Control Plan(2013-2017)

The Free Society, Health Country

goal
- 1. by 2020 :Less than 50 TB patiets
- 2. by 2025 :Less than 12 TB patiets
strategies
- 1. Shift a disease control paradigm to "Preventive Disease Control" and introduce latent TB checkupsand treatment systems
- 2. operate the life-cycle (tenth graders,40year olds) TB control porgrams for multiple-contac and high-risk groups
- 3. Greatly reduce TB inclidence by investing available resources (financila/human resources) intencively to break away from a developing country susceptible of TB
Legal basis
- Article 3(Duties of stute, Local Governments, Medical Doctors, etc.) of the Tuberculosis Prevenion Act.
- Article 11(Tuberculosis Examinations, etc) of the Tuberculosis Prevention Act.
The TB Prevention Project has been conducted with the vision of “TB Free Society, Healthy Country.”
The Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will prevent TB in advance by providing latent TB checkups and treatment to employees working at institutions such as medical institutions and daycare centers.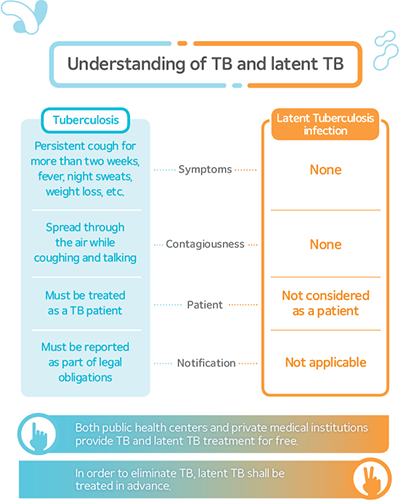
Understanding of TB and latent TBl
- Tuberculosis :Persistent cough for more than two weeks, fever, night sweats, weight loss etc. - Sympotoms - Latent Tuberculosis infection: None
- Tuberculosis : Spreead through the air wihile coughing and talking - Contagiousness - Latent Tuberculosis infection: None
- Tuberculosis : Must be treated as a TB patient - Patient - Latent Tuberculosis infection: Not considered as a patient
- Tuberculosis : Must be reported as part of legal obligations - Notification - Latent Tuberculosis infection: Not applicable
Both public health center and priate medical institutions provide TB and latent TB treatment for free. In order to eliminate TB, latent TB shall be treated in advance.

Tips for TB prevention
Check your 2week cough for TB test
Practice proper cough etiquette- Cover your mouth and nose width a tissue when you cough
- Cover your mouth and nose width your sleeve if you don't have a tissue
- Wash your hands under running water for over 30 seconds after coughing
