Objective
- To prevent the occurrence and spread of vaccine-preventable infectious diseases, prevent severe complications and deaths, secure diagnostic immunity for protection of vulnerable populations, thereby promoting public health and preventing community transmission
Direction
- Operation of a comprehensive surveillance system for vaccine-preventable infectious diseases
- Epidemiological investigation and patient management of vaccine-preventable infectious diseases
- Maintenance of measles and rubella elimination certification, and poliomyelitis eradication certification
Reporting and Notification System for Infectious Diseases
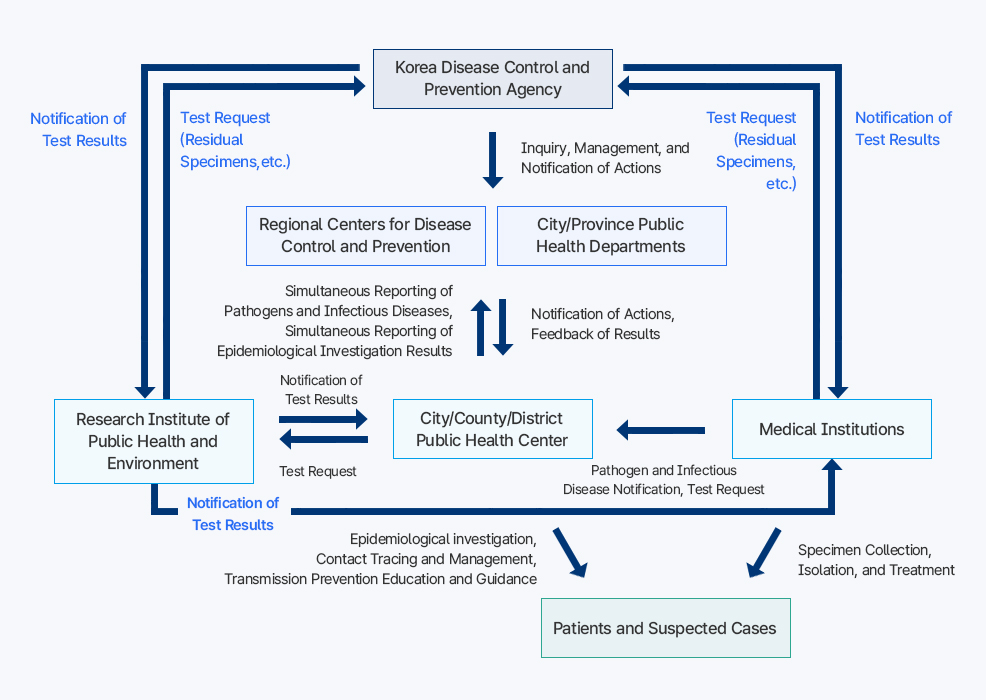
이 다이어그램은 감염병 발생 시 환자, 의료기관, 보건소, 보건환경연구원, 시·도 보건과, 권역별 질병대응센터, 질병관리청 사이의 신고 및 보고 체계를 설명한다. 1. 환자 및 의사환자는 증상이 있을 때 의료기관을 방문한다. 의료기관은 검체를 채취하고 격리 및 치료를 진행하며, 동시에 감염병 발생 사실을 시·군·구 보건소에 신고한다. 2. 시·군·구 보건소는 환자 접촉자 조사, 역학조사, 전파 예방 교육 등을 실시한다. 또한 검사 의뢰를 위해 보건환경연구원에 검체를 보내며, 결과를 통보받는다. 3. 보건환경연구원은 보건소로부터 검사 의뢰를 받고, 검사 결과를 다시 보건소에 통보한다. 결과는 질병관리청에도 보고된다. 4. 시·군·구 보건소는 감염병 신고와 검사 결과를 시·도 보건과 및 권역별 질병대응센터에 동시에 보고한다. 5. 시·도 보건과와 권역별 질병대응센터는 상황을 취합해 질병관리청에 전달한다. 6. 질병관리청은 최종적으로 모든 자료를 조회, 관리하며, 필요한 경우 조치사항을 각 기관(보건소, 시·도 보건과, 의료기관 등)에 통보한다. 전체적으로, 환자 발생 → 의료기관 신고 및 검체 검사 → 보건소 및 연구원 간 결과 확인 → 상위 기관 보고 → 질병관리청 관리 및 조치 통보의 순환 구조로 운영된다.
Operation of a Comprehensive Surveillance System
Reporting scope of vaccine-targeted infectious diseases
| Disease | Reporting Scope | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | Suspected Cases | Pathogen Carriers | ||
| Diphtheria | ○ | ○ | × | |
| Varicella | ○ | ○ | × | |
| Measles | ○ | ○ | × | |
| Pertussis | ○ | ○ | × | |
| Epidemic parotitis | ○ | ○ | × | |
| Rubella | Congenital | ○ | ○ | × |
| Acquired | ○ | ○ | × | |
| Poliomyelitis | ○ | ○ | × | |
| Haemophilus influenzae type b | ○ | ○ | × | |
| Pneumococcal infection | ○ | ○ | × | |
| Tetanus | ○ | × | × | |
Current Status of Occurrence
Table 3 | Current Status of Occurrence(2013-2024)
(unit:person)
| Year Name of Infectious Disease |
2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diphtheria | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Varicella1) | 37,361 | 44,450 | 46,330 | 54,060 | 80,092 | 96,467 | 82,868 | 31,430 | 20,929 | 18,547 | 26,964 | 31,892 |
| Measles | 107 | 442 | 7 | 18 | 7 | 15 | 194 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 49 |
| Pertussis | 36 | 88 | 205 | 129 | 318 | 980 | 496 | 123 | 21 | 31 | 292 | 48,048 |
| Epidemic parotitis | 17,024 | 25,286 | 23,448 | 17,057 | 16,924 | 19,237 | 15,967 | 9,922 | 9,708 | 6,358 | 7,737 | 6,425 |
| Rubella | 18 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 7 | 0 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Poliomyelitis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Haemophilus influenzae type b2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Pneumococcal infection3) | - | 36 | 228 | 441 | 523 | 670 | 526 | 345 | 269 | 347 | 431 | 451 |
| Tetanus | 22 | 23 | 22 | 24 | 34 | 31 | 31 | 30 | 21 | 23 | 24 | 29 |
Incubation Period, Infectious Period, and Patient Management Methods
| Category | Infectious Disease | Incubation Period | Infectious Period | Type of Management | Isolation (Precaution) Period | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Diphtheria | 1–10 days (Average: 2–5 days) |
If untreated, bacteria may be shed for 2–6 weeks. | Standard Precautions Droplet Precautions (Cutaneous Diphtheria: Contact Precautions) |
|
|
| 2 | Varicella | 10–21 days (Average: 14–16 days) |
From 1–2 days before the onset of rash until all skin lesions have formed crusts | Standard Precautions Airborne Precautions Contact Precautions |
|
|
| 2 | Measles | 7–21 days (Average: 10–12 days) |
From 4 days before rash onset until 4 days after | Standard Precautions Airborne Precautions |
|
|
| 2 | Pertussis | 4–21 days (Average: 7–10 days) |
At least 3 weeks after onset, until coughing stops (Until the 5th day after initiation of appropriate antibiotic therapy) |
Standard Precautions Droplet Precautions |
|
|
| 2 | Epidemic parotitis | 12–25 days (Average: 16–18 days) |
From 3 days before to 5 days after the onset of parotitis | Standard Precautions Droplet Precautions |
|
|
| 2 | Rubella | Congenital | - | During the period when the virus is shed in bodily fluids | Standard Precautions Contact Precautions (Avoid contact with pregnant women) |
|
| Acquired | 12–23 days (Average: 14 days) |
From 7 days before rash onset until 7 days after | Standard Precautions Droplet Precautions |
|
||
| 2 | Poliomyelitis | 3–35 days | From 11 days before symptom onset until 6 weeks after | Standard Precautions Contact Precautions |
|
|
| 2 | Haemophilus influenzae type b(Hib) | 2~10 days | As long as the bacteria are present in respiratory secretions | Standard Precautions Droplet Precautions |
|
|
| 2 | Pneumococcal infection | 1∼3days | As long as the bacteria are present in respiratory secretions | Standard Precautions |
|
|
| 3 | Tetanus | 3~21 days (Average: 7 days) |
(No human-to-human transmission) | Standard Precautions |
|
|
Vaccination
| Name of Infectious Disease | Vaccination | |
|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Adult | |
| Diphtheria Pertussis |
|
In cases with no prior vaccination history,
|
| Tetanus |
|
In cases with no prior vaccination history,
|
| Measles Epidemic parotitis Rubella |
Two doses of MMR vaccine
|
Adults without evidence of immunity should receive at least one dose *Measles: Individuals born before December 31, 1967, do not require vaccination (except for healthcare workers) |
| Poliomyelitis | A total of 4 doses(At 2, 4, 6–18 months, and 4–6 years of age) | Not routinely recommended for the general adult population; however, high-risk individuals without prior vaccination should receive a total of 3 doses (2nd dose administered 1–2 months after the 1st, and 3rd dose administered 6–12 months after the 2nd). *Schedule varies depending on age and vaccination history |
| Varicella | A single dose (at 12–15 months of age) *For individuals aged 13 years and older, two doses administered at 4–8 week intervals | Two doses administered at 4–8 week intervals |
| Haemophilus type b |
A total of 4 doses(At 2, 4, 6, and 12–15 months of age) *The recommended number of doses varies depending on the age at which vaccination is initiated. | Not routinely recommended for the general adult population; however, vaccination may be considered for high-risk groups. |
| Pneumococcal infection | A total of 4 doses of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV)(At 2, 4, 6, and 12–15 months of age) *The recommended number of doses varies depending on the age at which vaccination is initiated. | A single dose of pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV) for adults aged 65 years and older |
Maintenance of Measles and Rubella Elimination Eertification and Poliomyelitis Eradication Certification
(Background) Continued operation of the surveillance system following WHO certification as an elimination/eradication country and maintenance of elimination/eradication status through international cooperation
- (Measles and Rubella) Comprehensive case classification of reported cases and submission of WHO monthly reports (monthly), convening of the National Verification Committee for Measles and Rubella, and submission of the WHO elimination certification annual report (annually)
- (Polio) Operation of the acute flaccid paralysis surveillance system for early detection of polio and conducting polio testing for all reported cases, convening of the National Certification Committee of Polio Eradication, and submission of the WHO eradication certification annual report (annually)
