Definition of the National Immunization Program
- Essential vaccinations (based on the Infectious Disease Control and Prevention Act), supported by local governments and carried out through public health centers and designated medical institutions. The government determines the target and timing, and supports these vaccinations.
Program implementation system
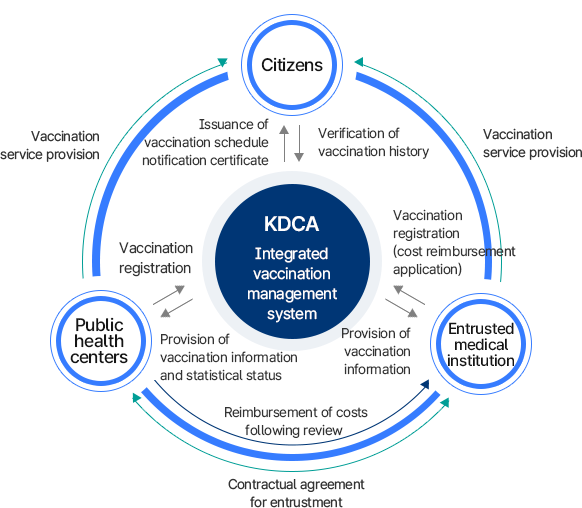
이 이미지는 예방접종 사업 추진체계를 보여주는 순환 구조도이다. 질병관리청 예방접종 통합관리시스템을 중심으로 국민, 보건소, 위탁 의료기관이 상호 연결되어 있다.
- 국민: 예방접종 서비스 제공을 받고, 접종 이력 확인과 접종일정 알림, 증명서 발급 가능.
- 보건소: 접종 등록을 담당하며, 접종정보와 통계현황을 질병관리청에 제공.
- 위탁 의료기관: 예방접종 서비스를 제공하고, 접종 등록 및 정보 제공. 또한 위탁계약을 체결하고 비용상환 심사·지급 과정을 거침.
- 질병관리청: 통합관리시스템을 운영하며 접종정보 관리, 통계 제공, 접종 내역 확인, 비용상환 심사 및 지급 업무를 수행.
의미: 예방접종 사업은 질병관리청을 중심으로 국민, 보건소, 위탁 의료기관이 상호 협력하며 운영되는 구조임을 나타낸다.
Targets of national vaccinations
- 19 types of infectious diseases for which local governments are responsible under the Infectious Disease Prevention Act for ensuring mandatory vaccination (as of June 30, 2025)
[Table 1] Infectious Diseases Subject to Mandatory Vaccinations
| Category | Disease | Category | Disease | Category | Disease |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Diphtheria | 8 | Epidemic parotitis | 15 | Hepatitis A |
| 2 | Poliomyelitis | 9 | Rubella | 16 | Human papillomavirus infection |
| 3 | Pertussis | 10 | Varicella | 17 | Group A rotavirus infection |
| 4 | Measles | 11 | Japanese encephalitis | 18 | Typhoid fever |
| 5 | Tetanus | 12 | Haemophilus type b | 19 | Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome |
| 6 | Tuberculosis | 13 | Pneumococcal | ||
| 7 | Hepatitis B | 14 | type b |
Targets of national vaccinations
[Table 2] Types of Vaccines and Targets for Infectious Diseases Subject to Mandatory Vaccination
| Disease | Targets of National Vaccination Program | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of vaccine | Target | ||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis | DTaP | Under 12 years old* | Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis |
| Tdap, Td | 11-12 years old | ||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Poliomyelitis | DTaP-IPV | 2, 4, 6 months, 4-6 years | |
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Poliomyelitis Haemophilus influenzae type b | DTaP-IPV/Hib | 2, 4, 6 months | |
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Poliomyelitis Haemophilus influenzae type b, Hepatitis B | DTaP-IPV/Hib/HepB | 2, 4, 6 months | |
| Tuberculosis | BCG(intracutaneous) | Within 4 weeks after birth | |
| Hepatitis B | HepB | At birth, 1 month, 6 months | |
| Poliomyelitis | IPV | 2, 4, 6-18 months, 4-6 years | |
| Haemophilus influenzae type b | Hib | 2, 4, 6 months, 12~15 months | |
| Pneumococcal | PCV | 2, 4, 6 months, 12~15 months | |
| PPSV | Those at high risk aged 2-12 years | ||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella | MMR | 12-15 months, 4-6 years | |
| Varicella | VAR | 12~15 months | |
| Hepatitis A | HepA | 12-35 months (Second dose 6 months after the first dose) | |
| Japanese encephalitis | IJEV(inactivated vaccine) | 12-23 months (second dose 1 month after the first dose), 24-35 months, 6-12 years | |
| LJEV(live vaccine) | 12~23 months, 24~35 months | ||
| Group A rotavirus infection | RV1 | 2, 4 months | |
| RV5 | 2, 4, 6 months | ||
| Pneumococcal | PPSV | 65+ years | |
| Human papillomavirus infection | HPV | Women aged 12-17 years, low-income women aged 18-26 years | |
| Influenza | IIV | 6 months to 13 years, pregnant women, 65+ years | |
| Typhoid fever | Vi antigen polysaccharide inactivated vaccine | Vi antigen polysaccharide inactivated vaccine | |
| Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome | Inactivated vaccine | Those at high risk | |
