Infectious Disease Surveillance
Meaning
The entire process of systematically and continuously collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data on infectious disease occurrences, pathogens, and vectors, and timely distributing the results to relevant parties for use in the prevention and control of infectious diseases.
Objectives
- Observing disease occurrence trends and predicting the potential magnitude of problems
- Early detection of infectious disease outbreaks and clusters
- Establishment of rapid and accurate response and control measures
- Provision of evidence for public health policy decisions
Types of Surveillance Systems
Mandatory Surveillance
A surveillance system mandated by Article 11 of the Infectious Disease Control and Prevention Act, requiring all physicians, dentists, oriental medicine doctors, heads of medical institutions, military unit commanders (military doctors), and heads of infectious disease pathogen confirmation institutions to report cases.
Sentinel Surveillance
A surveillance system operated under Article 16 of the “Infectious Disease Control and Prevention Act,” in which sentinel surveillance institutions are designated and reports from these designated institutions are collected.
Supplementary Surveillance
A surveillance system designed to supplement existing infectious disease surveillance, including diseases not classified as statutory infectious diseases but requiring monitoring of their occurrence and trends, in order to enable active and rapid response.
Classification System of Notifiable Infectious Diseases
Class 1 Infectious Diseases
Bioterrorism-related infectious diseases, or those with high fatality rates or a high risk of mass outbreaks, which must be reported immediately upon occurrence or epidemic, and require high-level isolation measures such as negative pressure isolation.
Class 2 Infectious Diseases
Considering their potential for transmission, these are infectious diseases that must be reported within 24 hours of occurrence or outbreak and require isolation.
Class 3 Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases that require continuous monitoring and must be reported within 24 hours of occurrence or outbreak.
Class 4 Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases, other than Class 1 to Class 3 infectious diseases, that require sentinel surveillance activities to investigate whether an epidemic is occurring.
Reporting and Notification System for Notifiable Infectious Diseases
Mandatory Reporters
| Doctors, dentists, oriental medicine doctors, and heads of medical institutions | Military unit commanders (military doctors) | Heads of infectious disease pathogen confirmation institutions | Other mandatory reporters |
|---|
Reporting and Notification System
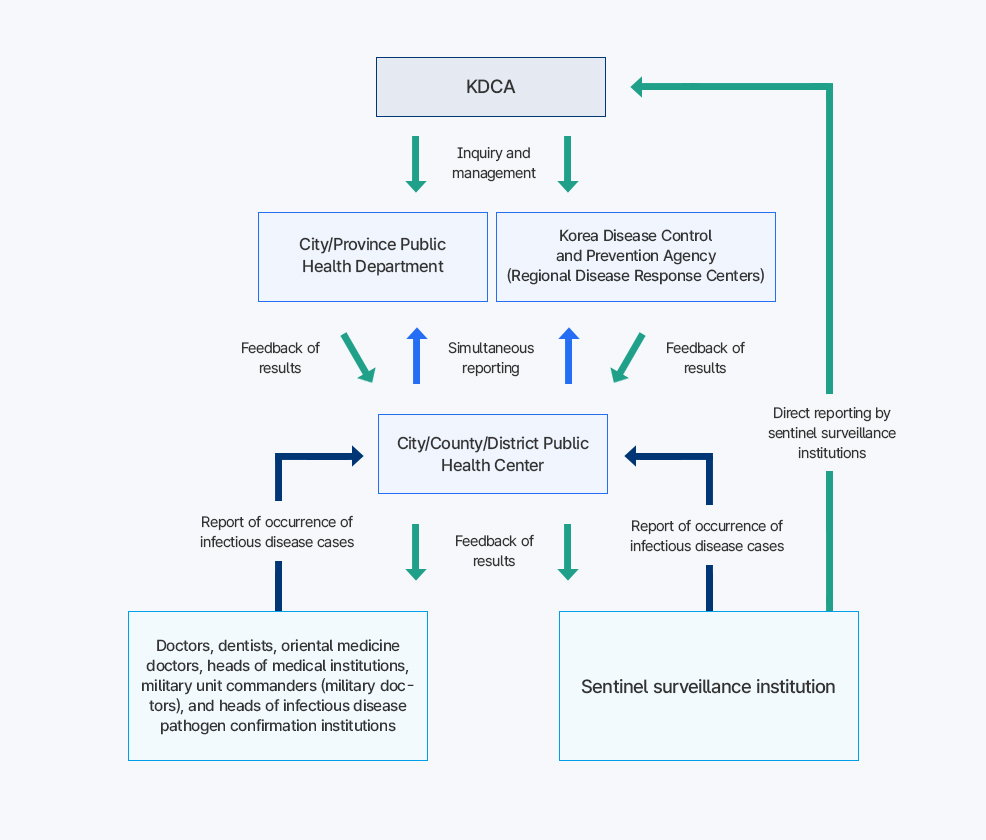
- Doctors, dentists, and oriental medicine doctors → Head of their medical institution → Report to the Commissioner of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) or the head of the local public health center
Doctors, dentists, and oriental medicine doctors not affiliated with a medical institution must report to the head of the local public health center. - Military doctors → Report to their unit commander → Report to the head of the local public health center
- Staff of an infectious disease pathogen confirmation institution → Head of the pathogen confirmation institution → Report to the Commissioner of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) or the head of the public health center with jurisdiction over the requesting institution
- Other mandatory reporters: In the case of occurrence of Class 1 to Class 3 infectious diseases → Request diagnosis or medical examination from doctors, dentists, or oriental medicine doctors, or report to the head of the local public health center.
Time of Reporting
| Category | Reportable Diseases | Reporting Period |
|---|---|---|
| Class 1 infectious disease |
|
Immediately |
| Class 2, Class 3 infectious diseases |
|
Within 24 hours |
| Class 4 infectious diseases |
|
Within 7 days |
| Adverse reaction after vaccination | Occurrence (diagnosis) of an adverse reaction case | Immediately |
Scope of Reporting
- Patient: A person exhibiting symptoms corresponding to the infectious disease, confirmed according to diagnostic criteria by a doctor, dentist, or oriental medicine doctor, or through laboratory testing by an infectious disease pathogen confirmation institution.
- Suspected Patient: A person suspected of having an infectious disease based on clinical symptoms and epidemiological links, who either has no test results meeting diagnostic criteria or is presumed to be infected according to criteria for presumptive diagnosis.
- Pathogen Carrier: A person who carries the infectious disease pathogen but shows no clinical symptoms.
