Overview
- Establish a basis for identifying the causes of injuries and formulating injury prevention policies through the operation of an injury management, investigation, and surveillance system.
Current Status of Injury Occurrence
- 3.55 million people (2023, 6.9% of the total population) experienced an injury in the past year, 1.23 million people (2023, 2.4% of the total population) were hospitalized due to an injury, and 30,000 people (2023, 7.9% of all deaths) died as a result of injuries*. * Among all causes of death, injury ranks 4th after cancer, heart disease, and pneumonia (Statistics on Causes of Death, 2023). The mortality rate due to injury is the 3rd highest among all OECD countries.
-
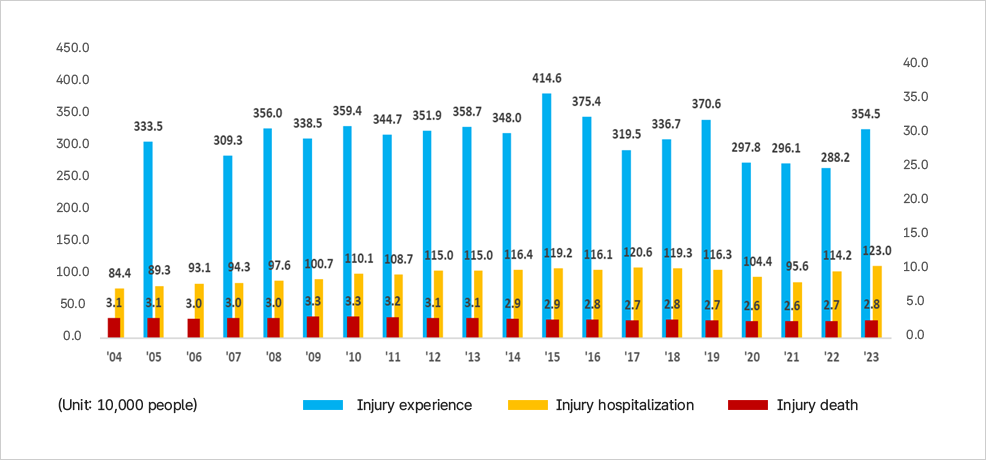
이 그래프는 2004년부터 2023년까지 손상 경험, 손상 입원, 손상 사망의 연도별 추이를 나타낸다.
- 손상 경험: 2004년 333.5명에서 2015년 414.6명으로 최고점을 기록한 뒤, 2020년 296.1명까지 감소했다가 2023년 354.5명으로 다시 증가했다.
- 손상 입원: 전반적으로 증가세를 보여 2004년 84.4명에서 2023년 123.0명까지 상승했다.
- 손상 사망: 연평균 약 2.6~3.3명 사이에서 비교적 일정하게 유지되었다.
의미: 손상 경험은 등락을 반복하면서 장기적으로는 감소 추세를 보이고 있으나, 손상으로 인한 입원은 꾸준히 증가하고 있다. 사망률은 큰 변동 없이 일정하게 유지된다.
-
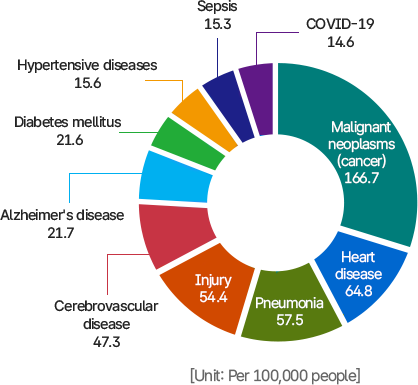
이 그래프는 인구 10만 명당 주요 사망원인별 사망률을 나타낸 원형 그래프이다.
- 악성신생물(암): 166.7명으로 가장 높은 비율을 차지한다.
- 심장질환: 64.8명
- 폐렴: 57.5명
- 손상: 54.4명
- 뇌혈관 질환: 47.3명
- 알츠하이머병: 21.7명
- 당뇨병: 21.6명
- 고혈압성 질환: 15.6명
- 폐혈증: 15.3명
- 코로나19: 14.6명
의미: 암이 가장 큰 사망원인으로 나타나며, 심장질환·폐렴·손상 등이 뒤를 잇는다. 감염성 질환(코로나19, 폐혈증)과 만성질환(당뇨병, 고혈압성 질환)도 주요 사망 요인으로 확인된다.
Source: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2023), In-depth Survey of Discharged Injury Patients (2023), Statistics on Causes of Death (2023)
- Among the socioeconomic costs* (KRW 148 trillion) attributed to diseases, the cost due to injuries (KRW 21 trillion) ranks first among all diseases (National Health Insurance Policy Research Institute, 2017). * Socioeconomic costs = Direct costs (medical expenses, caregiving costs, transportation costs) + Indirect costs (cost of premature death, loss of productivity)
Progress
- Since injuries are a preventable health issue, the World Health Organization recommended the establishment of a national injury surveillance system for injury prevention (1989).
- The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency established an injury investigation project in 2005 to identify the status of injury occurrence and prepare evidence-based data for injury prevention and management projects. Through this project, the scale and characteristics of injuries would be examined in hospitals.
- The Division of Injury Prevention and Management was newly established with the opening of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (September 2020).
- The Division of Injury Prevention and Management was newly established with the opening of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (September 2020).
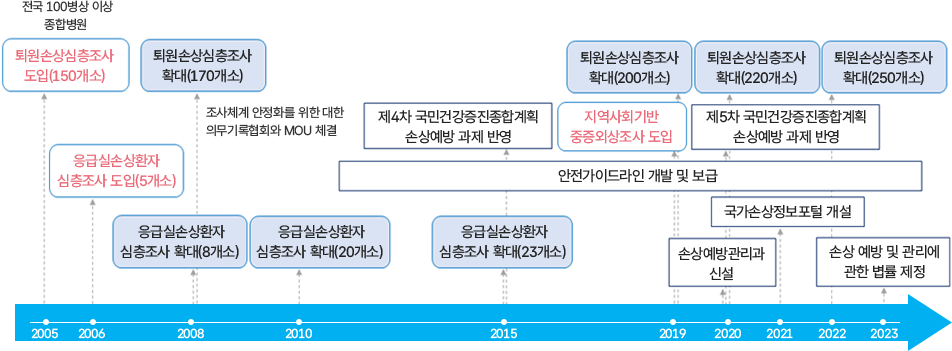
이 도표는 2005년부터 2023년까지 손상 경험·입원·사망 추이와 관련 제도의 변화를 연대표 형식으로 나타낸 것이다.
- 2005년: 퇴원손상심층조사(150개소) 도입
- 2006년: 응급실손상환자 심층조사(57개소) 도입
- 2009년~2015년: 응급실손상환자 심층조사 기관이 점차 확대(최종 233개소)
- 2013년: 제4차 국민건강증진종합계획에 손상예방 과제 반영
- 2018년: 지역사회기반 중증외상조사 도입
- 2019년: 안전가이드라인 개발 및 보급, 국가손상정보포털 개설
- 2020년: 손상예방관리과 신설
- 2021년: 제5차 국민건강증진종합계획에 손상예방 과제 반영
- 2022년: 손상 예방 및 관리에 관한 법률 제정
- 2005~2023년: 퇴원손상심층조사 기관이 지속 확대되어 250개소까지 증가
의미: 20년간 손상 경험·입원·사망의 추이를 지속적으로 모니터링하며, 제도적 기반 확충과 법제화로 손상 예방과 관리 체계가 강화된 것을 보여준다.
Purpose and Content of Investigation Projects
- (In-depth Survey of Discharged Injury Patients) To identify the scale and status of injury occurrence and establish a scientific basis for injury prevention and management by producing continuous and systematic statistics that are nationally approved
- (In-depth Survey of Emergency Department Injury Patients) To provide a basis for injury prevention and management by conducting timely, in-depth analysis and investigation of injury risk factors and vulnerable groups for each injury type
- (Community-Based Severe Trauma Survey) To provide basic data for improving the transport system and establishing emergency medical and disaster safety policies through comparative evaluation of the management of severe injuries and mass casualty incidents by region
Schematic of the Injury Investigation and Surveillance System by Injury Severity
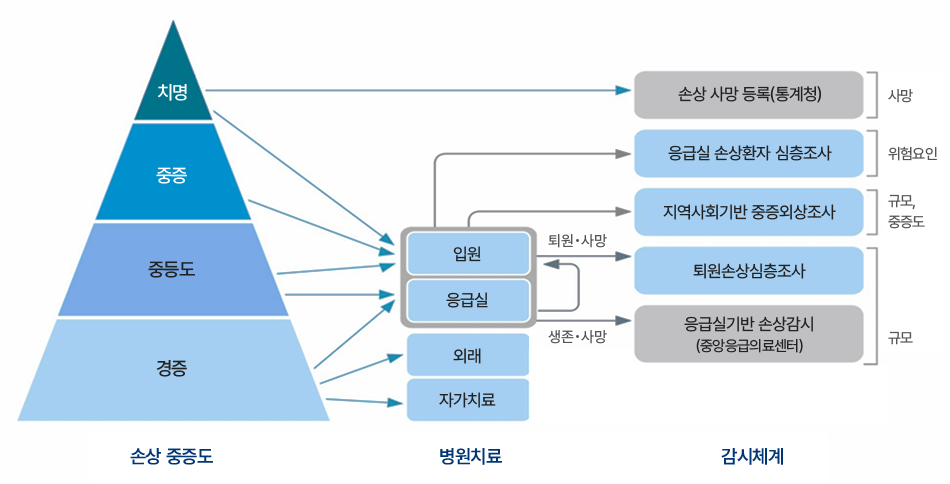
이 그림은 손상 중증도에 따른 병원치료 과정과 감시체계를 연계하여 나타낸 것이다.
- 손상 중증도: 경증 → 중등도 → 중증 → 치명 단계로 구분된다.
- 병원치료: 환자는 중증도에 따라 자가치료, 외래, 응급실, 입원으로 치료 과정을 거치며 생존 또는 사망으로 이어진다.
- 감시체계:
- 치명 단계는 손상 사망 등록(통계청)을 통해 관리된다.
- 중증 단계는 응급실 손상환자 심층조사, 지역사회기반 중증외상조사를 통해 위험요인과 규모, 중증도가 조사된다.
- 중등도와 경증은 입원과 응급실 치료 후 퇴원손상심층조사, 응급실기반 손상감시(중앙응급의료센터)를 통해 규모를 파악한다.
의미: 손상은 경증에서 치명까지 다양한 단계로 나타나며, 각각의 치료 과정은 국가 감시체계와 연계되어 손상 규모, 중증도, 위험요인, 사망률 등을 관리하는 데 활용된다.
Utilization and Policy Contribution
- Securing real-time injury surveillance data, including the status of injury patient occurrence and major causes
- Supporting the establishment of prevention policies by analyzing the characteristics of injury occurrence types by age and injury type
- Utilized for early identification of high-risk injury groups and prevention strategies.
- Utilized as evidence for injury prevention projects by related organizations and local communities, and for improving laws and systems.
